Network topology refers to the arrangement or layout of elements in a computer network. Such as computers, switches, routers, printers, firewalls, or other digital devices. It defines how nodes in a network are connected to transmit data from one node to another node. Network topologies are divided into two categories physical and logical. Physical network topologies pertain to the physical layout of the network and the physical medium of data transmission. Logical network topology refers to how data is transmitted between devices, irrespective of the physical design of the network.
Types of Network Topologies
There are different types of network topologies and each topology has its own characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.
- Point-to-point topology
This is a simple topology that connects two devices to communicate with each other. Physical connections relay one cable and wires. However logical connections use microwaves and satellites. This topology is speeder than other topologies, simple, and easy to implement and maintain. However that can use only a small area(noes should be close to each other), if the connection fails, the full network goes down.
- Bus topology
Bus topology is a network configuration where all nodes are connected to a single central cable, known as the bus or backbone. Data sent from any node travels along the bus to all other nodes in both directions until it reaches its destination. This topology is easy to install and extend, making it a cost-effective choice due to its minimal cabling requirements. However, it has limited scalability as performance degrades with the addition of more nodes, leading to increased data collisions. Additionally, troubleshooting can be difficult, and a failure in the central bus cable can disrupt the entire network, highlighting its single point of failure.
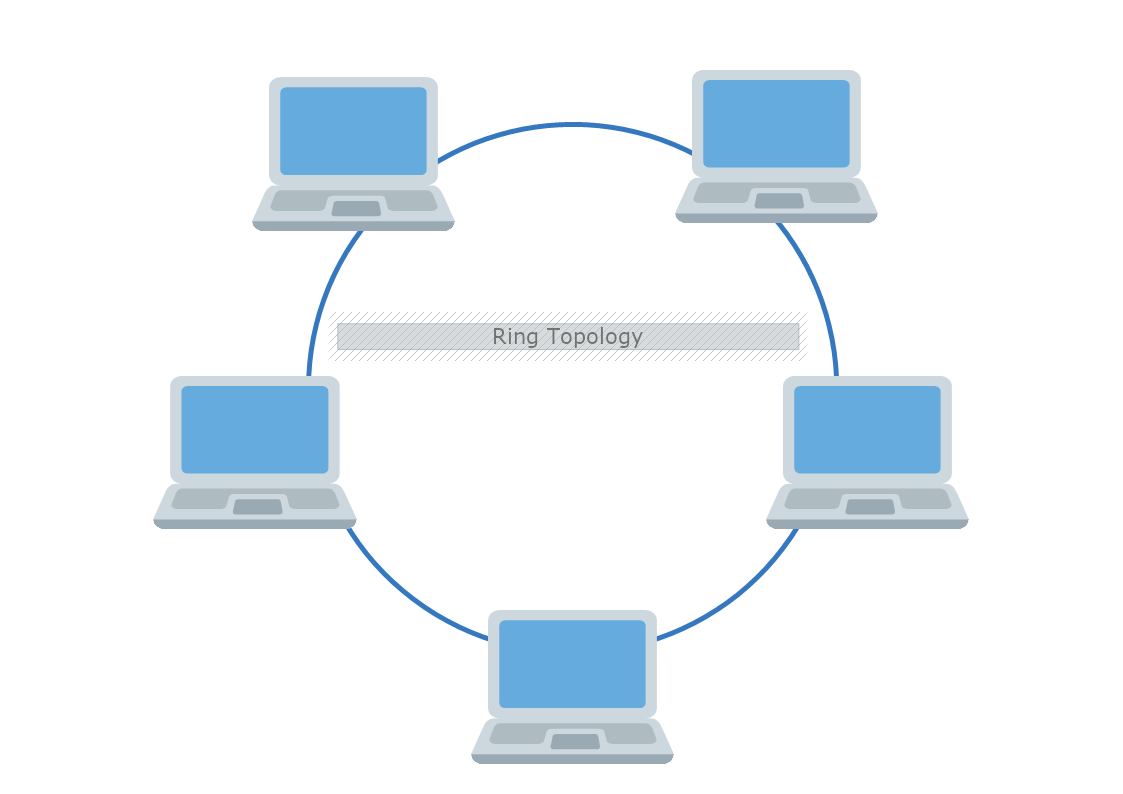
- Ring topology
A ring topology is a type of network configuration where each node is connected to exactly two other nodes, forming a circular data path. In this setup, data travels in a unidirectional or bidirectional manner around the ring until it reaches its destination. One of the key advantages of a ring topology is its ability to manage high traffic efficiently, as data packets can travel at high speeds and each node acts as a repeater to boost signal strength. However, a failure in any single node or connection can impact the entire network. Troubleshooting and maintenance can also be more difficult than other topologies due to the reliance on the continuous circular path.
- Star topology
Star topology is a type of network configuration where all nodes are connected to a central hub or switch, forming a star-like structure. In this setup, the central hub or switch acts as a repeater, facilitating data transmission between nodes. One of the primary advantages of star topology is its simplicity in installation and management, as each node has a dedicated connection to the hub or switch, making it easy to identify and isolate faults. Also, the failure of a single node does not affect the rest of the network, enhancing its reliability. However, the main disadvantage is that the network's functionality heavily depends on the central hub or switch if the hub fails, the entire network becomes inoperative. Moreover, star topology requires more cabling compared to some other topologies, which can increase the overall cost of the network setup.
- Tree topology
Tree topology is a network structure combining characteristics of bus and star topologies. In this configuration, groups of star-configured networks are connected to a linear bus backbone. This layout allows for the scalability of star topology while maintaining a manageable structure. One of the key advantages of tree topology is its scalability, as new nodes can be easily added without disrupting the existing network. Also, it is relatively easy to manage and troubleshoot. However, tree topology also has disadvantages, including the requirement for more cable compared to simpler topologies, which can increase installation costs. Moreover, a failure in the central backbone can compromise the entire network, leading to inoperative
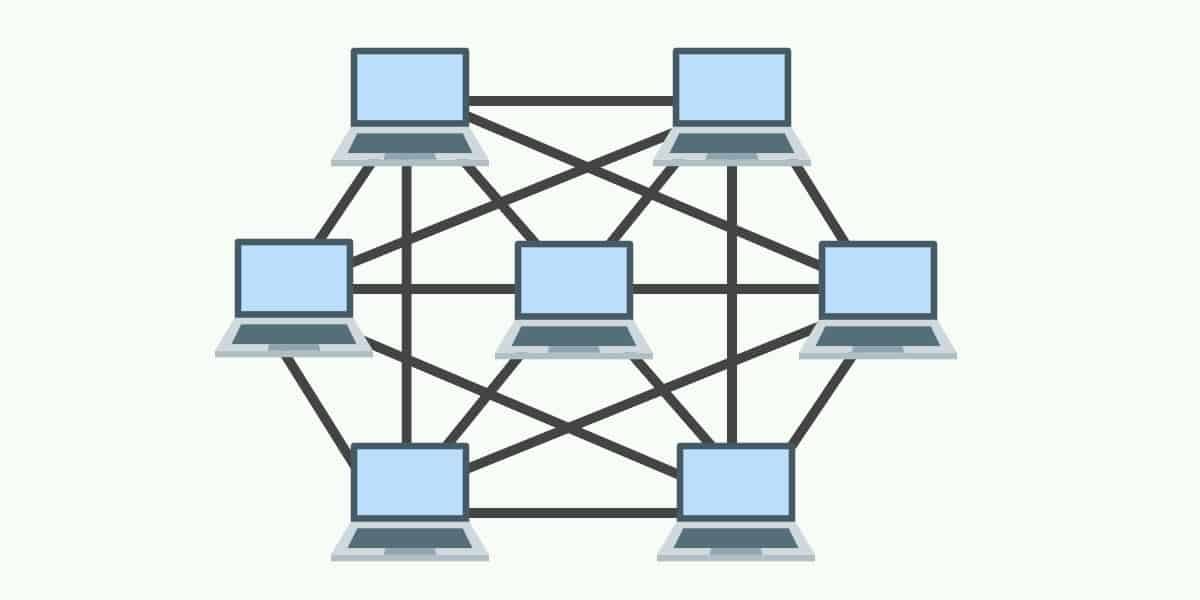
- Mesh topology
Mesh topology is a network design where each node is connected to every other node, allowing for multiple pathways for data to travel. This setup provides high reliability and redundancy, as data can be rerouted if one connection fails. The primary advantages of mesh topology include its robustness and fault tolerance, ensuring continuous network availability and data transmission. However, it also has some disadvantages, such as the high cost and complexity of installation due to the extensive cabling and hardware required for the numerous connections between nodes. This makes mesh topology less suitable for smaller networks with budget constraints.
- Hybrid topology
Hybrid topology is a combination of two or more different types of network topologies, such as star, bus, ring, and mesh, integrated to leverage the advantages of each while minimizing their drawbacks. This flexible approach allows for a more robust and scalable network design. The primary advantage of hybrid topology is its adaptability. it can be customized to fit the specific needs of various sections within an organization, enhancing performance and reliability. Also, hybrid topologies offer improved fault tolerance, as the failure of one segment does not necessarily affect the entire network. However, the main disadvantages include increased complexity and higher costs associated with the installation and maintenance the multiple topological structures.
***






0 comments:
Post a Comment